Code Scanning
 Secret scans are built on event-driven architecture. This means that every time a push is made to one of your selected repositories, Infisical will scan the modified files for any exposed secrets.
If one or more exposed secrets are detected, it will be displayed in your Infisical dashboard. An exposed secret is known as a “Risk”. Each risk has the following data associated with it:
Secret scans are built on event-driven architecture. This means that every time a push is made to one of your selected repositories, Infisical will scan the modified files for any exposed secrets.
If one or more exposed secrets are detected, it will be displayed in your Infisical dashboard. An exposed secret is known as a “Risk”. Each risk has the following data associated with it:
- Date: When the risk was first detected.
- Secret Type: Which type of secret was detected.
- Info: Information about the secret, such as the repository, file name, and the committer who made the change.
Responding to Exposed Secrets
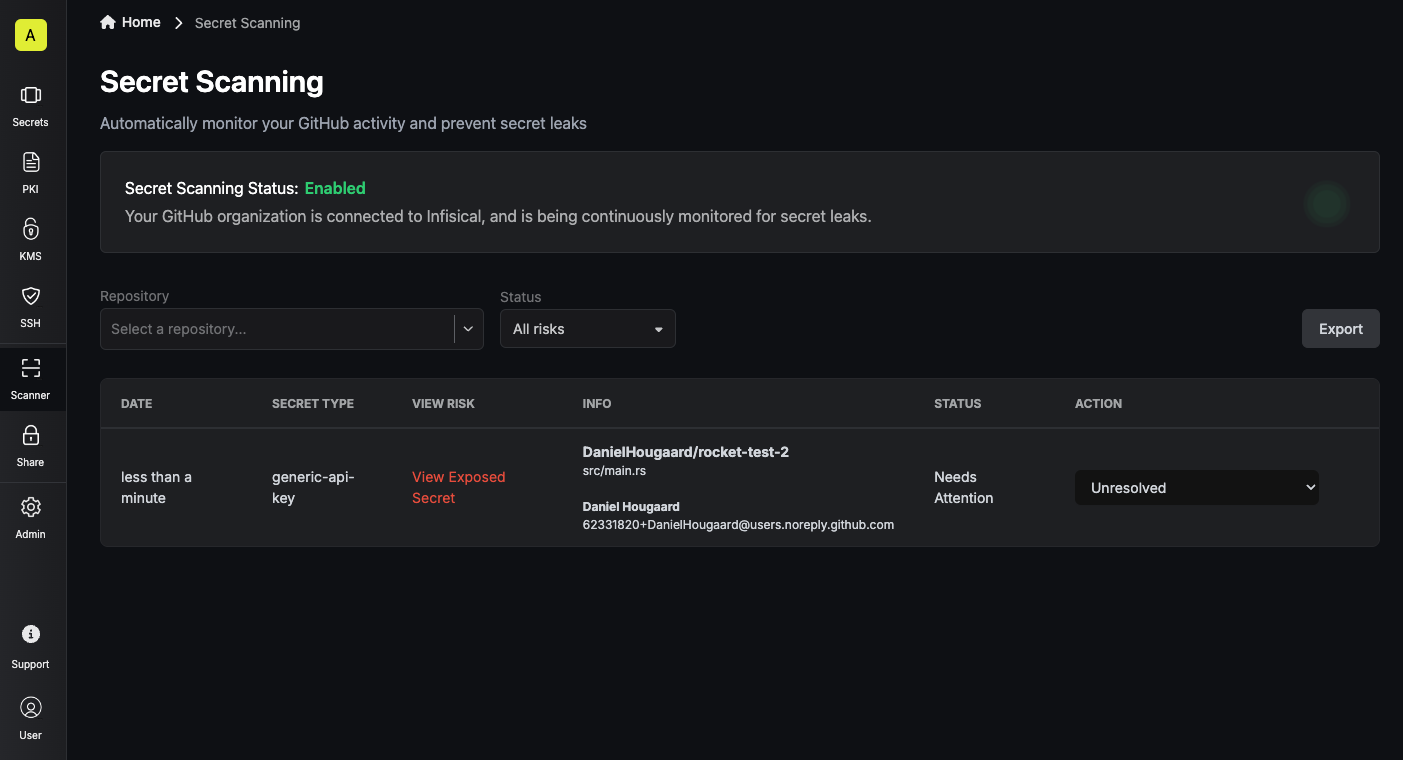
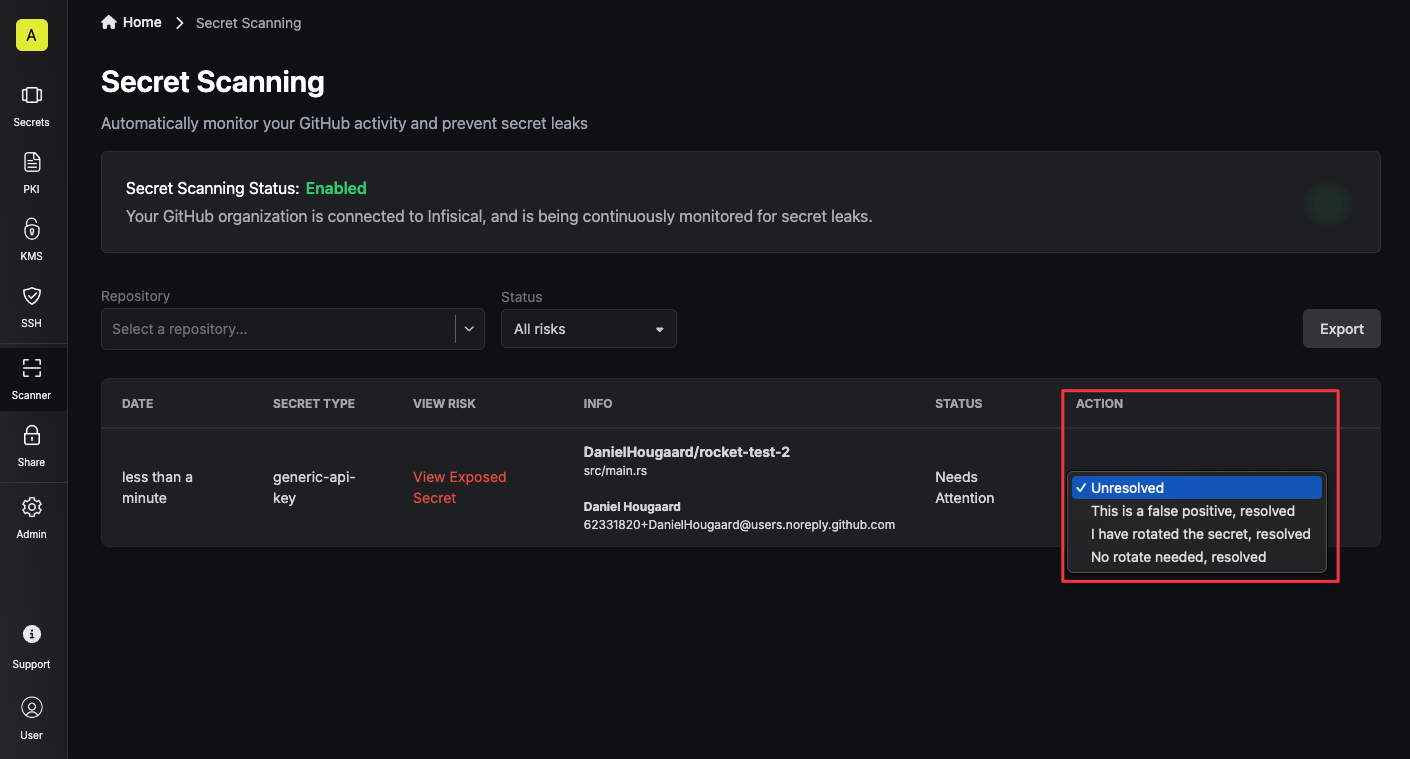
After an exposed secret is detected, it will be marked asNeeds Attention. When there are risks marked as needs attention, it’s important to address them as soon as possible.
You can mark the risk as Resolved by changing the status to one of the following states:
- This Is a False Positive: The secret was not exposed, but was detected by the scanner.
- I Have Rotated The Secret: The secret was exposed, but it has now been removed.
- No Rotation Needed: You are choosing to ignore this risk. You may choose to do this if the risk is non-sensitive or otherwise not a security risk.
Ignoring Known Secrets
If you’re intentionally committing a test secret that the secret scanner might flag, you can instruct Infisical to overlook that secret with the methods listed below.infisical-scan:ignore
To ignore a secret contained in line of code, simply addinfisical-scan:ignore at the end of the line as comment in the given programming.
example.js
.infisicalignore
An alternative method to exclude specific findings involves creating a .infisicalignore file at your repository’s root. You can then add the fingerprints of the findings you wish to exclude. The Infisical scan report provides a unique Fingerprint for each secret found. By incorporating these Fingerprints into the .infisicalignore file, Infisical will skip the corresponding secret findings in subsequent scans..infisicalignore

